Annuities explained: Get ready to dive into the world of annuities, where we break down the ins and outs of these financial products in a way that’s easy to understand and full of flair.
From the basics of what annuities are to the nitty-gritty details of how they work, this guide will have you feeling like an annuities expert in no time.
Overview of Annuities
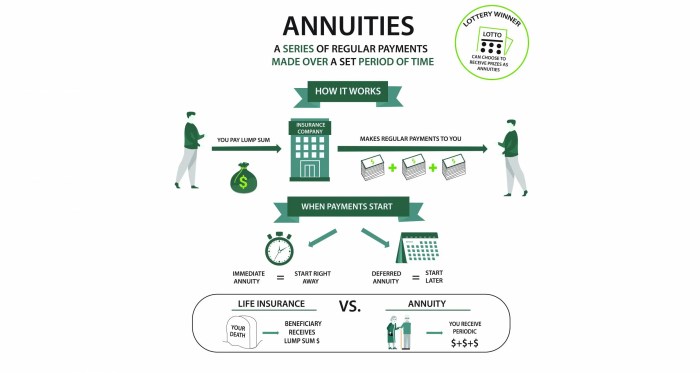
Annuities are financial products designed to provide a steady income stream in retirement or for a specific period. They work by an individual making a lump-sum payment or a series of payments to an insurance company, which then invests the funds and pays out a guaranteed income in return.
Types of Annuities
- Fixed Annuities: Offer a guaranteed interest rate for a specific period.
- Variable Annuities: Allow the owner to choose from a variety of investment options.
- Immediate Annuities: Begin payouts shortly after the initial investment.
- Deferred Annuities: Provide income at a later date, allowing for more significant growth.
Key Features and Benefits
- Tax-deferred Growth: Earnings in an annuity grow tax-deferred until withdrawn.
- Income Security: Annuities can provide a guaranteed income for life, protecting against outliving savings.
- Customizable Options: Various types of annuities offer flexibility in payouts and investment choices.
Parties Involved in Annuity Contracts
Annuity contracts involve three main parties:
1. Owner
The individual who purchases the annuity and makes contributions.
2. Annuitant
The person whose life expectancy determines the payout amount.
3. Insurance Company
The entity that manages the funds and pays out the income.
Annuity Structure: Annuities Explained
An annuity contract typically consists of the following components:
Premium
This is the initial amount of money paid by the annuitant to the insurance company.
Accumulation Phase
During this phase, the annuity grows tax-deferred as the funds are invested by the insurance company.
Annuitization Phase
This is when the annuitant starts receiving regular payments from the annuity.
Death Benefit
This ensures that if the annuitant passes away before receiving the full payout, their beneficiaries will receive the remaining amount. Annuities are funded through either a lump sum payment or a series of payments over time. The funds in the annuity grow over time based on the performance of the investments chosen within the contract. The growth is tax-deferred, allowing the annuitant’s money to compound without being taxed until withdrawals are made.
Payout Options in Annuities
- Life Annuity: Provides regular payments for the lifetime of the annuitant, ensuring income security.
- Joint and Survivor Annuity: Offers payments for the lifetimes of two annuitants, with the survivor continuing to receive payments after one annuitant passes away.
- Guaranteed Period Annuity: Pays out for a specific period, even if the annuitant passes away before the period ends, with the option to continue payments to beneficiaries.
- Variable Annuity: Allows payments to fluctuate based on the performance of underlying investments, offering the potential for higher payouts but also carrying more risk.
Pros and Cons of Annuities
When considering investing in annuities, it is important to weigh the advantages and disadvantages to make an informed decision.
Advantages of Annuities
- Guaranteed Income: Annuities provide a reliable source of income, either for a specific period or for life, giving you financial security.
- Tax-deferred Growth: Earnings on annuities grow tax-deferred until withdrawal, allowing your investment to potentially grow faster.
- Customization Options: Annuities offer various customization options, allowing you to tailor the annuity to suit your financial goals and needs.
- Death Benefit: Some annuities come with a death benefit, ensuring that your beneficiaries receive a payout if you pass away.
Drawbacks of Annuities
- High Fees: Annuities can come with high fees, including sales charges, administrative fees, and management fees, which can eat into your returns.
- Lack of Liquidity: Annuities often have surrender charges if you withdraw funds before a certain period, limiting your access to your money.
- Complexity: Annuities can be complex financial products, with different types and features that may be difficult to understand for some investors.
Comparison with Other Investment Options, Annuities explained
Annuities are often compared with other investment options such as mutual funds and individual stocks. While annuities offer guaranteed income and tax advantages, they may have higher fees and lack liquidity compared to these alternatives. It’s essential to carefully consider your financial goals and risk tolerance before deciding on the right investment vehicle for you.
Tax Implications and Regulations
When it comes to annuities, understanding the tax implications and regulations is crucial. Let’s break it down for you:
Taxation of Annuities
Annuities are tax-deferred investments, meaning you won’t pay taxes on the gains until you start receiving payments. This can provide a significant advantage by allowing your investment to grow faster without annual tax obligations.
- Withdrawals from annuities are taxed as ordinary income.
- If you withdraw funds before the age of 59 ½, you may be subject to a 10% early withdrawal penalty.
- When you annuitize your contract and start receiving payments, a portion of each payment will be considered a return of your initial investment (tax-free) and the rest will be taxable as earnings.
Tax Advantages and Consequences
Owning an annuity can have both advantages and consequences in terms of taxes. Here’s a breakdown:
Annuities can provide a tax-advantaged way to save for retirement, especially if you’ve maxed out other retirement accounts like 401(k)s or IRAs.
- One advantage is that there are no annual contribution limits for annuities, unlike 401(k)s and IRAs.
- On the other hand, annuities do not receive the same favorable capital gains tax rates as other investments like stocks or mutual funds.
Regulatory Framework
Annuities are regulated by state insurance departments and must comply with strict guidelines to protect consumers. Here are some key points:
Insurance companies offering annuities must be licensed and adhere to state regulations to ensure financial stability and consumer protection.
| Regulatory Body: | State Insurance Departments |
| Regulations: | Consumer protection, financial stability requirements, disclosure of fees and charges. |